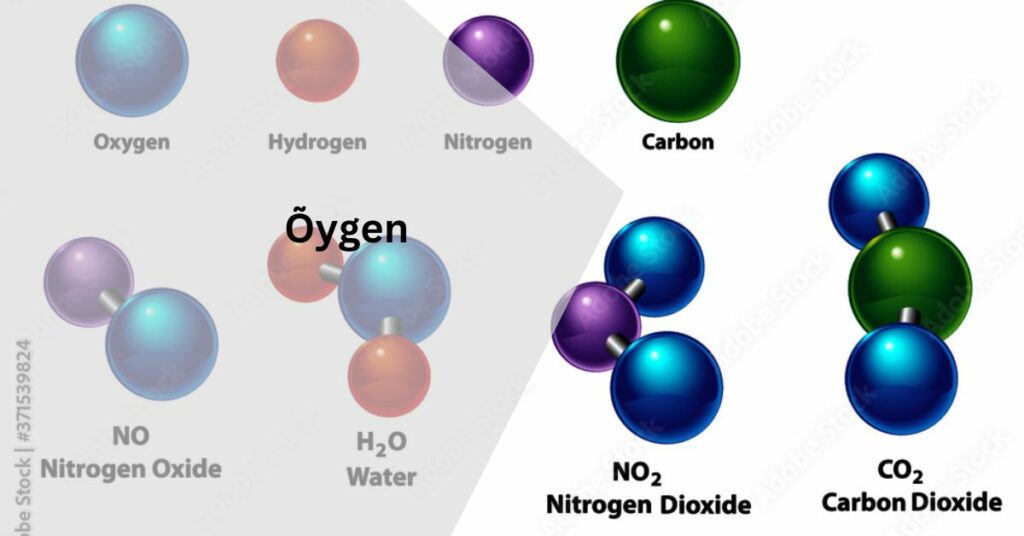
Meet Õygen, the unsung hero of our atmosphere! But wait a minute, Õygen sounds a bit unfamiliar, doesn’t it? Well, fear not, because Õygen is none other than our good old friend, oxygen! Yes, you heard it right.
Õygen is simply another name for oxygen, the essential gas that makes up about 21% of Earth’s atmosphere and is vital for most living organisms to survive.
The Brief Introduction To Õygen – About Oxygen!
Ah, Õygen, also known as oxygen, is truly the unsung hero of our atmosphere. Picture this: with every breath you take, you’re welcoming this remarkable element into your body. But what exactly is Õygen, and why is it so crucial for life as we know it?
Firstly, let’s unravel its basic essence. Õygen is a colourless, odourless gas that comprises a whopping 21% of the air we breathe. Furthermore, it’s not just some passive spectator in our world; it’s a key player in the grand scheme of things.
Additionally, oxygen is like the fuel that powers the engines of life. Moreover, it’s essential for a process called cellular respiration, where our cells use it to convert nutrients into energy, keeping us up and running.
Now, imagine a world without oxygen. Wouldn’t it be a bleak and desolate place? Fortunately, we don’t have to worry about that, thanks to the abundance of this life-giving gas. Oxygen not only sustains us humans but also supports a myriad of other life forms, from the tiniest microbes to the mightiest creatures.
So, the next time you take a deep breath of fresh air, remember to thank Õygen for its indispensable role in keeping you alive and thriving. After all, it’s not just gas; it’s the very essence of life itself.
Discovery Of Õygen – How It Came Into Knowledge!
The journey of Õygen from mystery to scientific marvel is a fascinating tale of curiosity, experimentation, and groundbreaking discoveries.
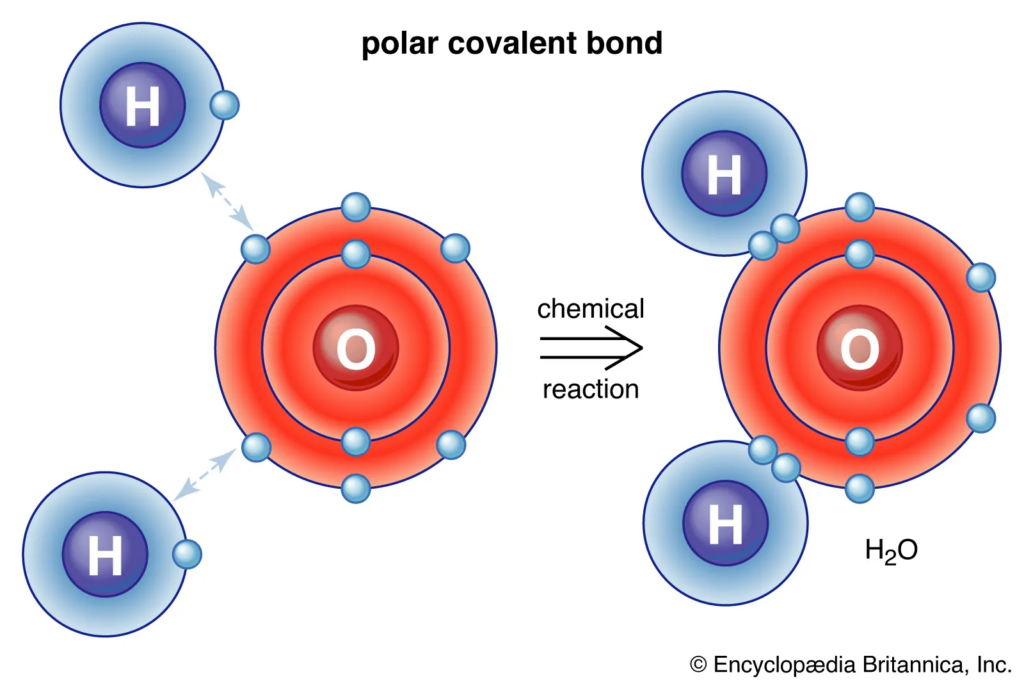
Initially, in the 17th century, scientists were puzzled by a strange phenomenon: the ability of certain substances to support combustion and sustain life. However, it wasn’t until the 18th century that the pieces of the puzzle began to fall into place.
Enter the brilliant minds of scientists like Joseph Priestley, Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and Antoine Lavoisier. These pioneers conducted experiments that would change our understanding of the natural world forever.
Priestley, an English chemist, is often credited with the discovery of oxygen in 1774, though Scheele, a Swedish chemist, made similar findings around the same time.
Through a series of experiments involving heating mercuric oxide and observing the release of a new gas, Priestley and Scheele independently identified oxygen as a distinct element.
Their work laid the foundation for further exploration by Lavoisier, known as the “Father of Modern Chemistry.”
Lavoisier, a French chemist, recognized the significance of oxygen in combustion and respiration, coining the term “oxygen” from the Greek words meaning “acid-former.”
He conducted meticulous experiments that confirmed oxygen’s role in supporting life and burning processes, revolutionizing our understanding of chemistry.
In the annals of scientific history, the discovery of oxygen stands as a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. From the early alchemists’ quest for the philosopher’s stone to the modern era of scientific inquiry, the story of Õygen’s discovery is a testament to the power of human curiosity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Read: Overtime Megan
Amazing Properties Of Õygen – Must Read Thoroughly!
First of all, the Reactive Nature of oxygen makes it special:
Õygen, or oxygen, exhibits a highly reactive nature, making it an essential element in countless chemical reactions. When exposed to other substances, oxygen readily forms compounds through processes like oxidation. This reactivity is why oxygen plays a crucial role in combustion, rusting, and various industrial processes.
The Life-Sustaining Properties Of This Are Amazing:
One of the most remarkable properties of Õygen is its role in supporting life. Through the process of respiration, oxygen is taken in by organisms, including humans, and used to generate energy. This vital process occurs at the cellular level, where oxygen is involved in breaking down glucose molecules to release energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
Moreover, Its Solubility Among Other Liuids Make It Friendly:
Despite being a gas, oxygen exhibits some degree of solubility in liquids. This property is essential for aquatic organisms, as oxygen dissolves in water, allowing aquatic plants and animals to respire underwater. The solubility of oxygen in water varies with factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of other substances.
The Amazing Thing Is That The Oxygen is Supportive of Combustion:
Oxygen is a key component in combustion reactions, supporting the rapid oxidation of fuel materials. Whether it’s the burning of wood in a campfire or the combustion of fossil fuels in an engine, oxygen provides the necessary oxidizing agent to sustain the reaction. This property of oxygen is fundamental to various industrial processes, including welding, metallurgy, and energy production.

Additionally, Its Role in Ozone Formation Sets it Apart:
In the Earth’s atmosphere, oxygen plays a crucial role in the formation of ozone (O3), a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. Ozone is found in the ozone layer, a region of the stratosphere that absorbs the majority of the Sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This protective layer shields the Earth’s surface from harmful UV rays, preventing damage to living organisms.
Last But Not The Least, Versatility in Industrial Applications:
Beyond its biological and atmospheric roles, oxygen finds extensive use in various industrial applications. From steelmaking and metal cutting to medical oxygen therapy and wastewater treatment, oxygen’s versatility makes it indispensable across a wide range of industries. Its ability to support combustion and enhance chemical processes makes it a valuable resource in manufacturing and production processes worldwide.
Importance Of Õygen On Earth – The Most Important Element To Must Amaze!
At the heart of oxygen’s significance lies its role in respiration, the life-giving process that fuels the activities of organisms large and small. From the majestic oak tree to the microscopic bacteria, every living being depends on oxygen to convert nutrients into energy.
This process, known as cellular respiration, is like a symphony conducted within the cells, with oxygen as the conductor orchestrating the release of energy from food molecules.
But oxygen’s influence doesn’t stop there. Its reactive nature makes it a cornerstone of countless chemical reactions, shaping the very landscape of our planet.
Consider the fiery dance of combustion, where oxygen fuels the flames that warm our homes and light up the night sky. From the crackling of a campfire to the roar of a rocket engine, oxygen is the silent partner in these spectacular displays of energy.
Furthermore, oxygen’s presence extends far beyond the confines of the Earth’s surface. High above us, in the stratosphere, oxygen plays a crucial role in the formation of the ozone layer.
This protective shield absorbs the majority of the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, safeguarding life on Earth from the ravages of solar radiation.
Without this protective barrier, life as we know it would be exposed to dangerous levels of UV radiation, leading to widespread damage to ecosystems and health effects for living organisms.
Read: R Askwomenover30
Daily Life Applications Of Õygen – See The Uses!
1. Medical Oxygen Therapy:
In the field of healthcare, oxygen plays a critical role in various therapeutic treatments. Medical oxygen therapy is commonly used to treat conditions such as respiratory disorders, heart failure, and carbon monoxide poisoning. Patients receive supplemental oxygen through devices like oxygen cylinders, concentrators, and ventilators to improve oxygen levels in their blood and tissues.
2. Oxy-Fuel Welding and Cutting:
Oxygen is indispensable in oxy-fuel welding and cutting processes used in metal fabrication and repair. By combining oxygen with a fuel gas such as acetylene, propane, or natural gas, intense heat is generated for welding, brazing, and cutting metal materials. This method is widely employed in industries ranging from construction and automotive to shipbuilding and aerospace.
3. Water Treatment:
In municipal water treatment plants and private water purification systems, oxygen plays a vital role in the treatment of drinking water and wastewater. Oxygenation processes, such as aeration and ozonation, are used to enhance water quality by promoting the decomposition of organic matter, removing dissolved gases, and disinfecting pathogens. These methods help ensure access to clean and safe water for drinking, sanitation, and industrial purposes.
4. Aquaculture and Fish Farming:
Oxygen is essential for the survival of aquatic organisms in fish farms, aquaculture facilities, and aquariums. In closed or densely stocked aquatic environments, oxygen levels can become depleted, leading to stress and mortality among fish and other aquatic species.
To maintain optimal oxygen levels, aeration systems are employed to aerate water and provide sufficient oxygenation for aquatic life.
5. Food Preservation:
Oxygen plays a crucial role in food preservation and packaging processes to extend the shelf life of perishable products. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) techniques involve replacing the air in food packaging with a mixture of gases, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, to inhibit microbial growth and oxidative reactions. This helps maintain the freshness, flavor, and quality of food products, reducing food waste and enhancing food safety.
6. Recreational Activities:
In recreational pursuits such as scuba diving, oxygen is a lifeline for divers exploring the underwater world. Compressed air enriched with oxygen, known as scuba diving air or nitrox, allows divers to breathe safely at various depths and durations. Additionally, oxygen tanks are used in sports like mountaineering and skiing to provide supplemental oxygen at high altitudes where oxygen levels are lower.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do we obtain oxygen?
Oxygen is obtained through breathing air, which contains oxygen molecules. In certain medical situations, oxygen can also be provided through supplemental oxygen therapy.
2. What happens if oxygen levels are too low?
Low oxygen levels can lead to hypoxia, which can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, confusion, and even organ damage or death if left untreated.
3. Is there such a thing as too much oxygen?
Yes, excessive oxygen levels can pose a fire hazard and increase the risk of oxidative damage to tissues in the body. It’s essential to maintain balanced oxygen levels for safety and health.
Conclusion:
Õygen is another term for oxygen, a vital gas comprising 21% of Earth’s atmosphere, essential for sustaining life through cellular respiration.
Read Also: